Search
Login
Recommended
We build the foundation with our own hands: calculating the load on the foundation. Foundations constructions: tape, reinforced concrete, block, rubble, columnar.
Before laying the foundation, work is carried out on the planning of the site. After mowing the grass, cutting down the bushes, after drawing up the general plan, it is necessary to fix the main elements of the site planning on the ground. The zero cycle includes a vertical layout of the site, the main purpose of which is to protect the foundation from water.
Having examined the site, we determine the presence or absence of nearby groundwater. If groundwater is close, drainage installation is necessary, for which drainage pipes are laid, installation is made drainage system.
Next, excavation works are carried out for digging a foundation pit, and the foundation and socle are arranged to a zero mark. The construction site should be 1.5-2 meters wider than the dimensions of the house in all directions. Very carefully you need to approach the issue of marking the center axes.
Content
- Foundation load calculation
- Foundation designs video
- Foundation laying
- Foundation defects and methods for their elimination
Foundation load calculation
Calculation of the load on the foundation for the house is carried out at the design stage of the structure. The purpose of these calculations is to determine the impact loads on the foundation. It must be remembered that the total load consists of permanent and temporary loads.
Constant loads include:
- the weight of the entire structure with all walls and roof, the weight of the foundation itself, equipment and furniture located in the house, people living in this area.
Variable loads include:
- atmospheric phenomena such as wind, snow.
To calculate the load, you need to know the specific gravity of the structure (for example, the specific gravity of one square meter of a frame-panel wooden house with a thickness of 150 mm. With insulation, is from 30 to 50 kilograms per square meter; and a log or block house has a specific gravity of from 70 to 100 kilogram per square meter). The specific gravity of one cubic meter of reinforced concrete or concrete foundation is 2550 kilograms per cubic meter.
The specific gravity of one square meter of attic wood flooring with insulation is up to 100 kilograms per square meter. The specific weight of the metal roof reaches up to 35 kilograms per square meter (depending on the thickness of the roof). In the calculation, the maximum number of specific gravity is taken to create a safety margin. The specific gravity of the building material is multiplied by the volume of the structure, thus we obtain the weight of the entire structure and multiply it by the load safety factor (1.2).
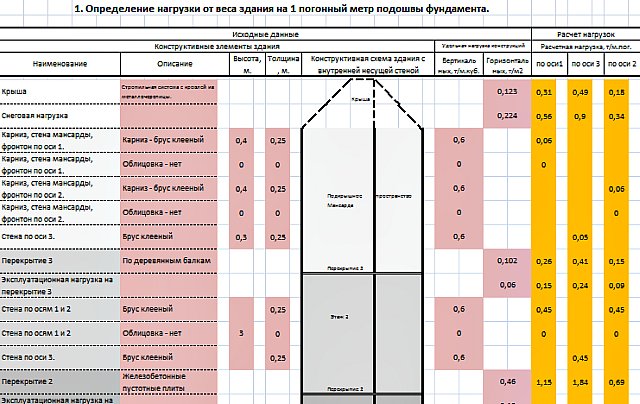
The magnitude of the variable load depends on the area of \u200b\u200bconstruction. For example, the snow load reaches from 80 kilograms per square meter to 560 kilograms per square meter (for example, Sakhalin Oblast). When calculating the total load on the soil, the weight of the foundation must be added to the weight of the house, having previously determined its dimensions. The depth of the foundation depends on the type of soil (not heaving — depth not less than 0.5 meters, regardless of the depth of freezing), heaving (sandy loam) - not less than part of the estimated freezing depth, but not less than 0.7 meters.
Each type of soil has its own value of bearing capacity without precipitation - this is the calculated soil resistance measured in kilograms per square meter. For example, sandy loam soil - 3 kilograms per centimeter square, clay soil from 2 to 4 kilograms per centimeter square depending on the porosity coefficient (the higher it is from 0.5 to 0.8, the lower the design resistance). Resistance of sandy soils, if coarse sand is from 6 to 5 kilograms per centimeter square, if sand is fine at low humidity, its resistance is from 4 to 3 kilograms per centimeter square.
Important! The main condition for laying the foundation is that the specific load on the plantar foundation should be less than the design resistance.
To have a good margin of safety, the resistance should be 15-20% more pressure. To comply with this condition, increase the reference area, with a columnar foundation, increase the diameter of the posts and their number, for strip foundations, increase the width of the tape.
Foundation designs
The foundation is selected depending on the weight of the structure, the depth of freezing of the soil, the bearing capacity of the soil. The most common are strip and column foundations. Both types can be made of monolithic or precast concrete or reinforced concrete, brick, butobeton.
strip foundation
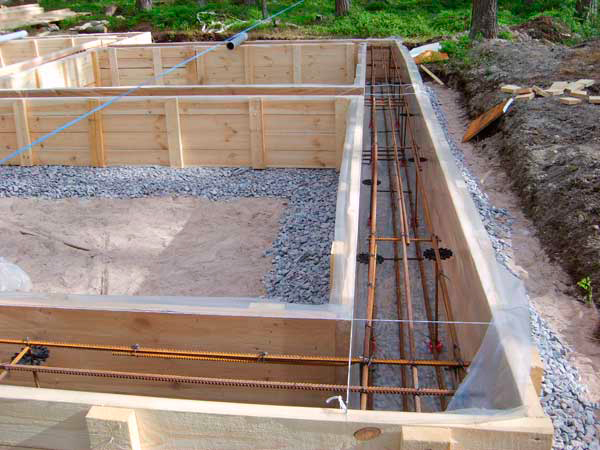

If the building being erected has heavy walls, several floors need to be built with a strip foundation. It is laid around the entire perimeter of the house, of course, a large amount of earthwork and a large consumption of building materials are assumed. During the construction of a monolithic foundation, formwork is used, which is installed in a dug pit.
reinforced concrete foundation
In the case of a decision to build a reinforced concrete foundation, it is required to install metal structures fastened together along the entire perimeter, thereby increasing the strength of the foundation. Then, along the entire perimeter of the foundation, concrete is poured in an even layer and compacted. High-quality concrete for a reinforced concrete foundation with a strength class from M100 to M500, as well as with practical functions of frost resistance and water resistance, can be ordered on the website beton174.ru.
prefabricated block foundation

Prefabricated block foundations are a combination of concrete or reinforced concrete blocks, which are pulled together with thick steel wire and laid on the mortar. This foundation is quickly being built and very reliable, but expensive.
brick foundation

Brick foundations are erected longer than monolithic and inferior to them in durability, such a foundation is made of ordinary solid red moisture-proof brick. The mortar used for bricklaying depends on the soil conditions and the calculated load on the foundation.
rubble foundation

The rubble foundations are built from rubble stones tightly joined to each other. This foundation is reliable, strong, durable, but the most expensive since the stones will have to be precisely selected and customized. Such a foundation is very good to use on wet soils since it does not allow moisture to pass through. The concrete foundation is made from a mixture of mortar and rubble stones of small and medium size. In the construction of this foundation, formwork is necessarily used, then the laying of rubble stone alternates, the compaction of this layer and the pouring of concrete between them.
column foundation
Columnar foundations are erected under buildings with light walls - wooden, frame.

When erecting such foundations, the following rules must be observed:
- poles are placed at all angles of the external walls of the structure, at the intersections of the internal walls with the external and at the intersection of all internal walls between the failure
- poles are installed around the entire perimeter of the building with a certain step, depending on the load, the step is from 1.2 to 2.5 meters
- between the posts is laid the base resting on the jumpers between the posts. The jumper performs two functions - serves as a screed for the pillars between each other and serves as the basis for the base. Basement insulates the subfloor from direct environmental influences, this affects the temperature and humidity directly in the house.
The price of reliable foundations, depending on the degree of their complexity, ranges from 70% of the cost of the house itself. But despite the costs, the most reliable and durable is a tape monolithic concrete foundation.
For small compact buildings, laying along the entire perimeter of the building directly onto the ground of concrete blocks and slabs is permissible. Heaving, thawing, subsidence of the ground practically do not threaten such a foundation.

If groundwater in winter does not rise closer than 2 meters to the boundary of freezing, for sandy, as well as clay soils of solid consistency, the depth of the foundation can be chosen regardless of the depth of freezing. In such cases, the minimum depth of the foundation: for sandy soil - 0.5 meters, for clay - 0.7 meters. The minimum thickness of the walls of the foundation of concrete is 35 cm, of rubble stone in mortar - 50.
Foundation laying
- during the construction of most foundation structures, concrete is used, and concrete, as you know, has the property of ripening, and the ripening period is not small, up to 30 days. At the end of all concrete work, a freshly prepared foundation must be maintained for a month without loads. To prevent drying of the top layer, it is desirable to close the concrete structure with some material, possibly roofing material. In order to prevent uneven drying of concrete, during the setting period, the foundation must be periodically watered. From all of the above, you can conclude that building a house on an unsupported foundation is fraught with the danger of cracks and distortions, all defects will appear very soon.
- the foundation waterproofing is very important, which means blocking the access of water to the entire surface in contact with the soil. The waterproofing of the foundation consists in coating with hot bitumen the entire surface, which is in contact with the soil, waterproofing is also laid between the foundation and the walls. To prevent moisture penetration, two layers of roofing material are laid, the first layer between the base and the zero level, the second between the base and the main wall of the house.

- the outer walls of the base must be protected from atmospheric influences, for this the outer walls of the base are plastered or lined with tiles suitable for outdoor use. To grout the foundation, it is good to add rubber-containing components to the cement mixture, for example, ash from burnt automobile tires. As a result of this grout, a beautiful and reliable coat for the base is obtained.
- when erecting a plinth, do not forget to provide a ventilation hole. They perfectly serve in the summer to air the underfloor, which additionally protects the building from dampness, and in winter they are closed for the same purpose.

- To protect the foundation from the effects of surface water, the construction of the blind area is necessary. The blind areas are built with a width of 0.75 to 1 meter, with an inclination from the walls of the basement. Good material is reinforced concrete, asphalt, concrete or well-compacted clay.
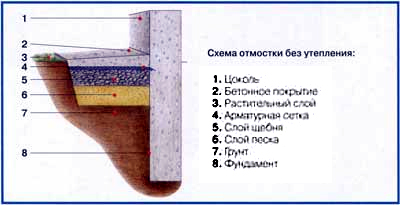
- in order to prevent subsidence of the soil, to preserve the bearing capacity of the foundation and to increase its strength, it is necessary to mount a rainwater drainage device from the roof, since rainwater from the roof falls onto the blind area, breaks it and the base, thereby gradually moistening the soil unevenly near the foundation.
Defects in the foundation and methods for their elimination.
A foundation may lose strength for several reasons:
- old age
- substandard materials
- low quality of construction work

Uneven subsidence is a major defect in foundations. This is expressed in the appearance of cracks of various shapes and very different directions, both on the foundation itself and on the walls of the house, various distortions of the house itself. All this is the result of mistakes and shortcomings in the construction of the foundation.
The reasons may be:
1. Wrong choice of the depth of the foundation, to fix this defect is very difficult and sometimes impossible at all. You can artificially increase the depth of the foundation; for this, soil is added along the entire perimeter of the foundation. This method can be effective if the subsidence is negligible.
2. If there is a rise in groundwater and this is known when laying the foundation, in this case, it is necessary to build a drainage system simultaneously with the installation of the foundation. If this phenomenon is discovered later, it is possible to arrange a drainage system after the construction of the building, to plant trees that effectively collect moisture from the soil (poplar, willow, broom, etc.).
3. Uneven load on the foundation from the side of the structure, can also cause uneven subsidence of the foundation. For example, the main house is much heavier than the veranda. To avoid further deformation, if the building is already built, it is necessary to separate the foundation of the veranda and the house. To do this, lay between the foundations boards impregnated with bitumen. To prevent this error, knowing that the veranda is much easier at home, it is better to build separate foundations.
4. If you incorrectly assessed the capabilities of an existing foundation and additionally increased the number of storeys of the house, thereby increasing the load on the foundation, which caused uneven subsidence of the foundation, it is possible to eliminate this defect. This elimination will cost the owner of the house a decent amount, it is necessary to strengthen the foundation by increasing the bearing area of \u200b\u200bthe foundation. To do this, a trench equal to or slightly deeper than the height of the foundation digs around the foundation, holes are drilled in the main foundation, where pieces of reinforcement 10-12 mm thick are inserted. with a protrusion outward to the width equal to the width of the additional foundation, the more pins, the better the coupling of the main and additional foundations, then the trench is filled with concrete, the work is hard but effective.
5. In brick foundations, piled on a mortar of lime, the adhesion of the mortar to the brick decreases with time, overhaul of the foundation is necessary, replacement with a new one. Here is an example of replacing the foundation of an old log house. The house was very skewed, on the one hand the lower crowns completely grew into the ground. Before starting the repair, they dismantled the Russian stove, completely freed the house from heavy things, cleared the approaches to the four outer corners, even dismantled a small veranda, which prevented the lifting of the house and the construction of a new foundation.
First, the builders made a dig under the very sagging wall, pulled out the crumbling old foundation, then using 30 ton jacks, lifted the two most sagging corners of the house. To install each jack, they made a dig so that the jacks did not go into the ground under the weight of the house, put them on concrete slabs 450x450 mm in size. 10 cm thick. Using a laser level, precisely mark the height by how much you need to raise each corner of the house. After lifting to the desired height, the jacks were replaced with pieces of timber and boards. Then they dug a trench under the foundation with a depth of 50-60 cm, a width of 35 cm, made the formwork. Sand was poured into the prepared pit with a layer of 15 cm, concrete was poured into the installed formwork, metal waste was used to reinforce the concrete, cobbles were added to the concrete and all this was compacted, a strip foundation was made with curbstones at the corners for three weeks, then, a month later, when the concrete stood, the temporary supports were removed.





