Search
Login
Recommended
Gooseberry - choose a variety, grow it correctly, get acquainted with known diseases and pests
The summer period gives us valuable fruits and berries, among which it is worth noting gooseberries. This shrub gives very useful berries, they are widely used in medicine and cosmetology, suitable for freezing, preserves, juices and compotes. Berries contain a large number of vitamins and minerals, stimulate metabolism, prevent anemia, lower cholesterol ... In addition, the cultivation of gooseberries is not complicated by features, and a variety of varieties will allow you to choose a shrub based on the personal preferences of the gardener.
Content
- Gooseberry Varieties
- Gooseberry Planting
- Care video
- Gooseberry propagation video
- Pests and gooseberry diseases
Gooseberry Varieties
Gooseberries are distinguished by the size and color of berries, resistance to diseases and frost, the number of thorns on the shrub and the fruiting period. The most popular varieties in our country are Kolobok, Malachite, Sirius, White Triumph. Less well-known varieties of Hinnonmaki Rot, Invicta.

Ripe berries of gooseberry variety Kolobok of medium shade of medium size, spines on the bush are rare, the variety is ripe. Malachite is resistant to frost, aromatic berries, spikes are rare, the variety is resistant to powdery mildew. Gooseberry Sirius bearingless variety with berries up to 3 cm, mid-season, resistant to frost and fungal diseases. White Triumph is distinguished by high productivity and large berries, it is resistant to powdery mildew, unfortunately, the variety is subject to freezing at a temperature below - 18 gr.
Hinnonmaki Rot with medium-sized fruits of dark pink color, resistant to diseases and frosts, late ripening variety. Invicta gooseberry is resistant to frost and powdery mildew, aromatic berries are large, ripen in July-August.

All gooseberry varieties reach an average of 1.3 m in height, shrubs are sprawling, the taste of the berries is sweet and sour, not all varieties differ in their special aroma. Almost all gooseberries are resistant to frost, only during flowering in the second half of April, the bush is susceptible to frost. To gooseberry consistent varietal qualities for a start it is necessary to plant it correctly.
Gooseberry Planting
Gooseberry seedlings should be purchased from trusted sellers, avoiding buying in the markets. In specialized stores there are certificates, reliable sources, on seedlings you can find useful information about the variety and its features.

Gooseberries prefer fertile, slightly acidic soil with a pH of 6.2-6.7. The position of the shrub is the sun or half-sun in the southern areas, if previously infected plants grew on the site, soil treatment is carried out.
The best predecessors of gooseberries are root crops and legumes, these plants can grow not only before planting a bush, but also after, next to gooseberries. Gooseberries also respond well to the introduction of manure and mineral fertilizers.

The optimal planting period is autumn, from late September to early November, the depth and width of the pit for planting is 45 cm, the distance between bushes is 2.5 - 3 m, between rows of 0.5 m, it is advisable to install a support structure for each shrub, it will be easier to collect berries, and the branches under their weight will not bend to the ground.

During autumn planting, the roots of shrubs have time to take root well, gooseberries adapt better to weather conditions. Spring planting produces worse results, gooseberries grow slowly, entry is delayed during the period of full fruiting, but there are also advantages, for example, spring planting of gooseberries with a low frost resistance will allow the shrub to gain strength until severe frosts.
Care
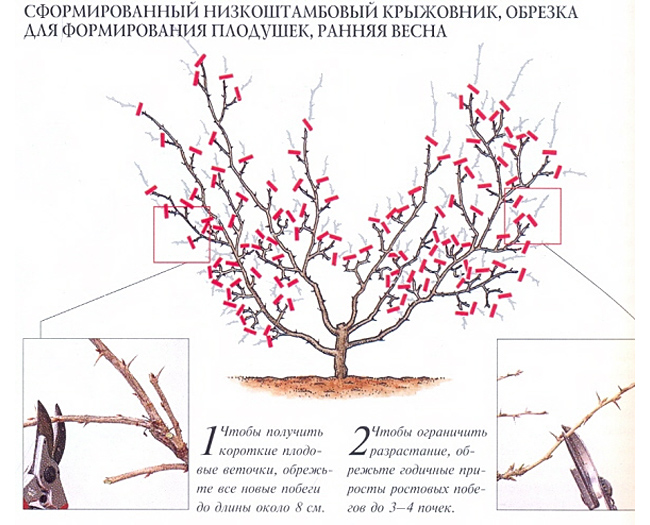
After the autumn planting, in the beginning of spring (late February - March), the lateral branches are reduced by 10 - 12 cm, which contributes to the rejuvenation and high productivity of the bush, a similar pruning of gooseberries is repeated for the fifth year. The stems of the previous year are reduced each year to 5 cm, dry branches and growing inside the bush are also cut.
Growing gooseberries, weeding around the bush with the help of tools is eliminated - the roots of gooseberries are close to the soil surface and are easy to damage, weeds are destroyed manually. Mulching of the soil is welcome, gooseberries do not tolerate drought, and covering with agrotextile or pine bark under a shrub will reduce moisture evaporation and weed growth. The lack of watering affects the health of the shrub and its fruiting, especially gooseberries need watering during flowering and ripening of fruits.
Every spring, nitrogen fertilizers are applied, in the fall - potassium and phosphorus.
Gooseberries begin to bear fruit in the third year after planting, in full force after 4-5 years, fertilizer application and proper pruning will help reduce these periods. The fruits of the early varieties ripen in mid-June, the late ones in August, pick berries when they acquire the desired color and become soft. Ripe berries remain on the shrub for up to 20 days, fresh gooseberries are stored for about a month at a temperature of 0-2 C.
Gooseberry propagation
Gooseberries are propagated by seeds, cuttings and layering, before breeding gooseberries make sure that the mother shrub is healthy. At home, propagation by layering is simpler, in spring, the lower branches are bent to the soil and dug, in the fall, cuttings are cut from the mother bush and planted in a new place.

For cuttings in early summer, young shoots with 3-5 buds are used, the finished cuttings are planted on the prepared site and often watered, in the fall the seedling will be ready for transplanting. Propagation by seeds is rarely used, shrubs obtained from seeds will bear fruit no earlier than five years, they require special care - shelter for the winter and preventive protection against pests and diseases.
Pests and gooseberry diseases
Powdery mildew is the most dangerous disease of gooseberries, leaves and fruits are covered with white, and then a gray coating, the berries become unsuitable for consumption. For prevention and treatment, weekly spraying of bushes with liquid (1 l) is practiced with 1 tbsp of vegetable oil and table soda. How to treat gooseberries in advanced cases? Here, unfortunately, it cannot cope without fungicides.
Anthracnosis, septoria are similar symptoms - leaves are covered with brown spots and if untreated fall early, the fungus hibernates on the leaves, so they are collected and burned. To combat the disease, Bordeaux fluid is used (50 g per 5 liters of water), the bush is sprayed during the disease and after harvest.
The most common pests of gooseberries are ticks and aphids. Aphids carry viral diseases, feed on leaves and shoots of plants, which leads to their deformation. Fighting aphids - spraying with infusion of garlic or onions, attracting beneficial insects - lacewings and ladybirds.
Spider mites multiply massively in dry and hot weather, it is difficult to notice insects right away, since they feed on a plant on the underside of leaves. On the tops of the shoots you can see a cobweb, gooseberries turn yellow, weakened shrubs do not grow and bear poor fruit. Against this pest, shrubs spray with infusion of garlic with dandelion leaves and onions.





