Search
Login
Recommended
Roof anti-icing systems. The main element of the design is the heating cable, which ensures reliability and efficiency of heating.
With the onset of winter, every homeowner gets the opportunity to check the reliability of all the structural and technical features used in the construction of his private property. But such a seemingly planned inspection can lead to disappointing consequences. The appearance in the arsenal of competent homeowners de-icing systems will protect not only the roof and drainage systems from unnecessary repairs, but also your budget from unforeseen expenses.
Content
- De-icing systems - a universal means of protection against frost
- The need to install anti-icing systems video
- The device of anti-icing systems
- The principle of the system
- Heating cable - the basis of the de-icing system
De-icing systems - a universal means of protection against frost
Roof anti-icing systems can rightfully be considered a universal means of protection against snow accumulations and ice on the roof, gutter systems and cornices. Winter-spring period with enviable periodicity pleases the owners of private cottages with alternating snowfalls, thaws and frosts, which leads to a significantly increasing load on the roof. Until a certain stage in the development of innovative technologies in construction, the only way out of an annual emergency was considered to be a mechanical way to clear the roof of ice. But the vicious circle, the main links of which are scrap and shovel, allowed to break the innovative developments that led to the emergence of anti-icing systems.

The need to install anti-icing systems
Before considering the mechanism of functioning of the roof heating system, it is necessary to explain why, from the point of view of the operational capabilities of the roof, the formation of ice is dangerous.
Firstly, the increased level of mechanical pressure on the structural elements of the roof leads to a rapid decrease in its operational life.
Secondly, the fall of ice on the downstream automobile, architectural objects can be the result of significant material costs, as well as cause irreparable harm to human health.

And thirdly, the retention of a large amount of moisture within the roof can lead to massive leaks and damage to residential premises located directly under the roof, as well as parts of building facades.
Innovative developments involving the heating of the roof and gutters allow to extend the operational life of the roof, eliminate damage to facades and gutters, and also significantly save on repairing the roof structure.
The device of anti-icing systems
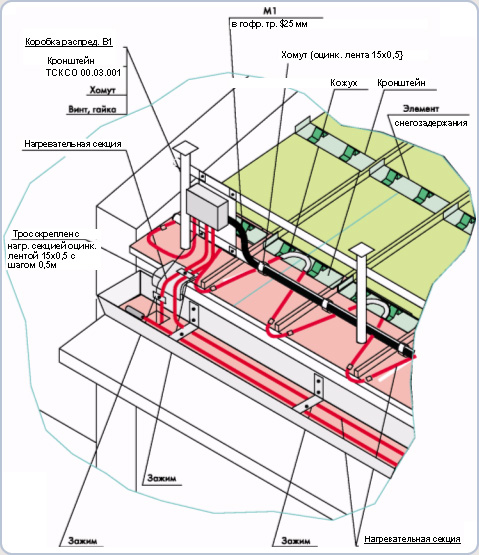
The design scheme of the anti-icing systems includes three components, which are presented:
1. Distribution network or information transmission network;
2. Directly by the heating system, which includes a set of heating cables and devices for their strengthening on the roof;

3. A control system that contains a control cabinet, sensors for determining precipitation and temperature indicators, special-purpose thermostatic control units and starting devices.

The principle of the system
Timely power-up and the same disconnection of the heating cable on the roof areas prone to potential ice formation and along the course of snowmelt snow drains is the main principle of the functioning of the roof heating system.

By heating the roof areas where ice accumulations are possible, it is possible to prevent freezing of the roof as one of the main problems in the winter-spring period. This process is controlled by a temperature regulator, the specificity of the device of which implies automatic switching on while there is plus temperature and precipitation. With the simultaneous presence of both conditions in the environment, the inclusion of automatic heating helps to prevent the formation of ice on the roof and icicles.

In order to prevent unforeseen interference during the operation of the anti-icing system, it is necessary to carefully consider all the nuances of its arrangement. Given that the main constructive solution of roof heating systems is the use of electrical wiring with additional heating elements and control mechanisms, it is necessary to draw up a plan diagram according to which the system cable will be laid.

The implementation of the simplest functional principle of heating systems is possible when laying the cable in the drainpipes and gutters, as well as along the lower edge of the ramps, in other words, along the entire length of the path that melt water passes. It is also worth noting that the installation technology of the system provides for a free path for the outflow of moisture formed.

An important point in ensuring the absolute operability of the system heating of the roof is compliance with the specified power range. Horizontal sections of the roofing surface need heating, which is equipped with a specific power of the heating system of at least 180 W / sq. m, while the linear power range is about 20 30 W per section of a drainpipe one meter long. The increase in the length of the drain provides for a directly proportional increase in the power limit of the cable, which is the main unit of the heating part of the anti-icing system.

Heating cable - the basis of the de-icing system
The functional and constructive basis of the de-icing system is the cable involved in providing reliable systemic heating of the roof. In connection with the structural and technological features of roof heating systems, the prevailing types of cables in the structure of the anti-icing system are recognized as resistive and self-regulating.
Cables of a resistive type for heating roofs are characterized by stable indicators of resistance and power throughout their length and consist of a metal conductor, an insulating layer and an outer sheath. Professionals advise to clearly distinguish several species groups of resistance cables (resistive), the main representatives of which are zone and armored cables. The zonal design of the cable is appropriate for the arrangement of heating systems of a large drainage system and pipes with high diametrical indicators. It is preferable to use armored when installing heating of flat roofs made of reinforced concrete and concrete drainage trays, since the level of permissible temperature conditions of such cables is several times higher than the limits of zonal type cables.

The advantages of resistance cables are obvious. The high level of specific heat, the possibility of multilayer laying and high elasticity contribute to the widespread use of resistive cables in structural solutions for roof heating systems.
But as with any other materials, this type of cable can be found to have several drawbacks. A constant level of resistance throughout the cable contributes to an unjustified waste of electricity, and given the fact that the need for heat generation varies in different sections of the roof, this can be considered a disadvantage of the resistive design. The need for continuous cleaning of garbage and fallen leaves from the roofs also relates to the negative aspects of resistive cables.

This problem can be solved by installing anti-icing systems based on self-regulating cables. The thermal energy generator in the cables of this type is represented by a carbon-filled semiconductor-type polymer matrix. Such design features make it possible to automatically generate heat throughout the cable system, taking into account temperature fluctuations and the conditions of the physical environment in which the cable is laid.
Calculation of the power of the cable heating system is carried out taking into account the climatic zone, the type and material of the roof, as well as the features of thermal insulation. The main power indicators of heating cables are specific heat dissipation equal to 20-30 W / m and power at the level of 250 W.






