Search
Login
Growing champignons in a garden, mushroom cultivation technology, useful tips
It can be argued that representatives of champignon mushrooms are one of the most common edible mushrooms, there are more than 60 species. You can meet representatives of this family on all continents except Antarctica, they can grow not only in the forest, but also in the field, in the garden or in the meadow, in open areas in the steppe and in the desert. Active growth of fungi, provided sufficient nutrient and soil moisture in the middle lane can be observed from May to October. Having studied the conditions for growing champignons, you can easily master the technology of their preparation in the country, not only in the warm season, but also in winter. Use champignon to prepare various dishes, including original sauces. In the Mediterranean countries they are preferred to be used raw when preparing salads.
Content
- Mushroom description
- Where mushrooms are grown
- Substrate Preparation video
- How to sow champignon mycelium video
- How to grow champignons - care tips video
- How to grow mushrooms in the beds
Mushroom description
Since champignons are classified as saprophytes, the soil enriched with humus can be considered the ideal place to live, so they can often be found on a forest edge covered with a thick layer of fallen foliage or on a pasture manned by cattle. Successful industrial cultivation of the fungus will also require the creation of an environment rich in biodegradable organic compounds.
For industrial cultivation, two varieties of champignon are used:
- four-spore two-ring,
- double cows.
Meadow and field mushrooms are bred less often.
Champignons - hat mushrooms, they have a central leg, its height is 5-6 cm. The mushroom hat usually has a diameter of 5 to 10 cm, but individuals with a hat more than 30 cm in diameter can be found. At the beginning of growth, the fungus has a bell-shaped or spherical hat, then it becomes convex-spread.
By the color of the hat, mushrooms are divided into several groups:
- milk color
- white
- cream
- brown, the so-called royal champignons.
As the fungus grows, the hue of its plates changes, if the young fungus has a delicate, pinkish color, then the more adult one has a reddish-brown color, then they become maroon.
Where mushrooms are grown
To grow champignons in a suburban area, you can use:
- beds and trenches dug in the garden - in the summer,
- basements, greenhouses, hotbeds, dugouts, sheds - in the cold season.
Ideal conditions can be considered rooms with an air humidity of about 85-90% and temperatures above 12C, preferably in the range from 13 to 30C. Regarding the illumination, it should be noted that champignon is not picky about it; a good crop can be obtained by growing mushrooms in a dark room.
Substrate Preparation
The main attention should be paid to preparing the nutrient medium, i.e. substrate. Compost is made by mixing straw bedding with fresh horse manure. Often use straw obtained from winter cereal crops with a mixture of horse and cow manure. But if necessary, pork or sheep dung or chicken droppings are also successfully used, straw is replaced by chopped stalks of corn or leaves fallen from trees.
Experts warn: use rotten straw and rotted manure in no case!
To improve the quality of the substrate, it is added:
- ammonium sulfate or urea,
- alabaster, gypsum or chalk as mineral additives.
The stock of manure or chicken manure intended for the preparation of a nutrient medium is stacked in piles on a leveled and covered roofing material, or concrete site, well-packed, then covered - it should be excluded the possibility of contact with sunlight or rain water. You can also use a barn for storage. Prepare the substrate in advance, about a month before you need to lay it in boxes, trenches or beds.
The straw mixed with manure is composted, i.e. provoke its decomposition under the influence of microorganisms. Since the host plant is not required for the growth of champignons, it is possible to grow champignons at home only if the champignon compost contains enough:
- nitrogen compounds obtained from manure
- carbon, which in large quantities contains wheat and rye straw,
- calcium, which is found in the chalk supplement.
In addition, the quality of compost is enhanced by the addition of complex mineral fertilizers and meat and bone meal. Structuring the compost mass and preventing its caking is facilitated by the addition of gypsum.
The successful cultivation of mushrooms largely depends on what recipe and how accurately compost is made in accordance with it. Experienced mushroom growers have their own time-tested formulas of the highest quality substrate. Beginning amateur hybrids can use the following formulas: add 12 kg of fresh wheat straw to gypsum or chalk in an amount of 1 kg, ammonium sulfate 25 g, 8 kg of fresh cow or horse manure, or chicken droppings. Depending on the type of manure, preparation of the substrate will take from 23 to 26 days.
If mushrooms are grown throughout the year, then you will need to prepare a room with a temperature higher than +10 degrees - this is the optimal temperature for preparing the substrate. If mushrooms are planned to be grown in the summer-autumn period, then a moisture-proof canopy over a concrete or asphalt-covered area will suffice - the mass should not have contact with the ground.
The technology for composting is as follows:
- chop the straw and moisten it,
- after two days, it is laid in layers, alternating a layer of straw and a layer of manure,
- as they are laid, the straw and manure are moistened with water, with previously diluted mineral fertilizers.
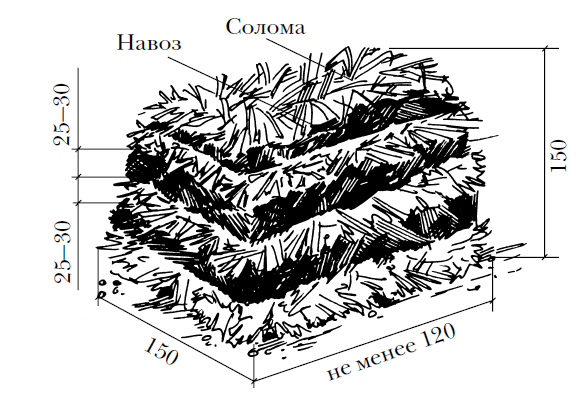
The optimal heap size is 1.5 m in height and the same in width. When forming a pile-pile, it should be remembered that at least 100 kg of straw should be contained in it - with a smaller amount of fermentation, it may or may not slow down at all - the heating temperature will be too low. The more substrate is prepared simultaneously in the pile, the higher will be its quality and the greater the amount of mycelium can be obtained.
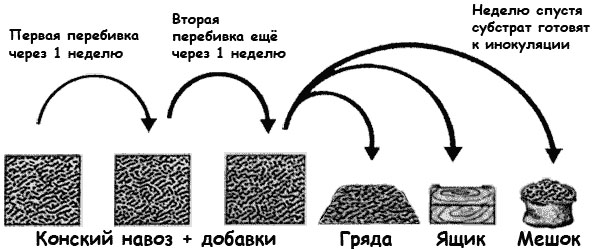
A heap breakdown will need to be done after 5-7 days, during its implementation additional moistening of each layer will be required. The interruption is carried out in such a way that the areas located outside move inside the shoulder and the inside out. In the process of preparing one portion, it is recommended to perform the chopping 4 times - each of them will lead to equalization of the time required to complete the process - the fact is that it occurs at different depths in different ways. Humidification is carried out daily, but at the same time one should not give more water than the formed shoulder can hold.
Usually, the readiness is determined by the disappearance of the ammonia odor and the acquisition of a mass of dark brown. As a rule, this happens on the third day after the last pile break. Now it is possible to form compost beds, with a layer thickness of at least 10 cm, for planting mycelium, or lay out the compost in special containers or bags made of polyethylene with a layer of 20 cm.
How to sow champignon mycelium

Experienced mushroom growers recommend buying mycelium from well-known manufacturers - if the technology was broken during its production, or its storage and storage were not carried out correctly, it is very likely that the filamentous formations, called hyphae, died - in this case, the mycelium will not grow. The best option is the vegetative propagation of mushrooms, when sowing mycelium obtained in laboratory conditions. Most often, for planting mycelium, rooms with constantly high humidity and a stable temperature, for example, a cellar, are used. If the mycelium is purchased in the form of compost blocks, then you do not need to compost yourself.
Only cooled compost is suitable for seeding mycelium - to lower the temperature it is laid out with a thick layer and wait when it drops below +25 degrees. This condition is recommended to withstand - otherwise, the subsequent increase in temperature after seeding will lead to inhibition of the development of the mycelium or its death.
Sowing is carried out according to the following standards: for 1 ton of compost 6 kg or 10 liters of grain mycelium will be required. If you grow mushrooms for your own consumption, in small quantities, then you can focus on such norms: one two hundred gram package of mycelium per 40 kg of substrate. Sow it in the prepared holes having a depth of about 8 cm and located with a pitch of at least 15 cm between rows and holes in the row itself. Nearby rows should have holes staggered. Sowing can be done manually or using special cutters and a packer.
To maintain stable humidity, the substrate, after sowing the mycelium, is covered with straw mats or burlap. To prevent mycelial diseases every third day, it is recommended to treat it with a two percent formalin solution.
In case of cultivation using non-covering technology, the air is humidified by watering the floor and walls - moisture entering the compost can cause mycelium disease. The best temperature for the growth of mycelium + 23 C, while the temperature of the substrate should be in the range of 24-25 degrees.
How to grow champignons - care tips
For the growth of mycelium under optimal temperature conditions, it will take 10-12 days. During this period, a large number of thin white hyphae will appear in the substrate. If the threads become visible on the surface, they need to be covered with a layer of peat mixed with a small amount of chalk. It is recommended to adhere to the following proportion: for 6 parts of peat, take 1 part of chalk and 3 parts of dolomite chips. The thickness of the poured layer should be about 3-4 cm.
After 4-5 days after this procedure, it is recommended to reduce the room temperature to + 17C. You should also start watering the top layer of compost from a watering can. The amount of water should not be large - it should moisten only the top layer, without going into compost.
It is very important that during the sowing of the mycelium and during the cultivation process, an air flow is established in the room - if the carbon dioxide content in the air exceeds the norm, the growth of mushrooms will slow down. Humidity throughout the process should be kept at 60-70%. Fruiting of mushrooms will begin on about twenty to twenty-fifth days after planting the mycelium. Fruiting occurs together, breaks between its peaks can become 3-5 days. The duration of the period is from 50 to 60 days.
Successful cultivation of champignons ends with the harvest, they are carried out manually, as if twisting the mushroom from the mycelium. It is advisable that the air temperature during the collection period be from +12 to +18 C. So that no spots appear on the mushroom caps, the room is well ventilated before starting work. Experienced mushroom pickers determine the best time for harvesting by observing the film connecting the champignon hat with the leg - it needs to be well stretched, but it is undesirable to allow it to break. After harvesting, the mushrooms are sorted, laying damaged and overripe specimens.

Harvest every other day or every day. When fruiting ends with a substrate, it will be possible to fertilize the soil on the beds.
How to grow mushrooms in the beds

For growing champignons, you can also use ordinary beds in the open. This method is more economical, it does not require large cash costs. The main task is the proper preparation of compost. To prepare it, you can use horse manure or chicken. In the process of its preparation, and it lasts about a month, you will need:
- mix the manure, pour it with a hot urea solution and condense,
- after 10 days, shake the shoulder, add chalk and form a new pile, already less dense,
- after the next 10 days add superphosphate, compact again and wait until the substrate reaches a friable state and turns brown.
A layer of substrate up to 35 cm thick should be laid out on the bed, planting mycelium can be carried out at a compost temperature of the order of +23 + 25 ° C, the air temperature should not be lower than +20 C. The size of the mycelium for planting in one hole should be the size of a chicken egg, optimal the depth of the hole is 5 cm. After planting, the holes are covered with a substrate, watered, covered with a layer of film or newspapers - to preserve moisture in the soil.
After 20 days, when the mycelium appears, the shelter is removed, the bed is covered with a layer of peat mixed with turf soil. Fruiting in the open ground lasts for two months, the crop should be harvested in a timely manner - otherwise the mycelium will be greatly depleted. Watering the site should be carried out twice a week, heated with water from a watering can.





