Search
Login
Drills for concrete, brick, stone, how to choose the right advice from the master
Nowadays, many different devices and tools are used to carry out the necessary construction work. One of the very first was the drill. Holes for various purposes remain in demand today: hang a picture, lay a wire, assemble and fasten furniture, fix a baseboard and much more. For each of the materials in which you want to make a hole, you need to use a drill suitable for this material. So what are the drills?
Content
- Drill classification video
- The design of the working part
- Shank design video
- Drill Materials
- Drill Covers
- Different materials different drills
Drill classification
The drill has been used by people for more than two millennia. During this time, it has overcome a considerable path from a simple wooden stick to a high-tech product.
Conventionally, each drill is divided into three parts:
- working part;
- neck;
- shank.

Drills are classified according to several criteria:
- construction of the working part;
- shank design;
- according to the manufacturing method;
- by appointment;
- on the processed material;
- for coating drills.
The design of the working part
The working part of the drill is selected depending on the material in which it is necessary to drill a hole:
Twist or screw drills the most popular and common, familiar to every layman. The working part of the drill consists of two cutting edges, which are formed by the intersection of two screw surfaces. At the top of the drill, the edges form an angle, depending on the material being processed, its value is changed. For soft metals and wood it is 80-90, for steel and cast iron 116-118, for stone concrete, brick 130-140. One of the varieties of twist drills are drills for deep drilling. The tool has soldered or drilled technological holes for supplying coolant to the working area.

Flat (feather) drills used for drilling holes in wood and plastic. The cutting part, made in the form of a blade, allows you to drill holes of large diameter and depth.

Core drills made in the form of a hollow cup, the material is selected only along the perimeter of the drilling.

Centering used when drilling center holes. They are divided into four types: A, B, C, R. The type of drill depends on the angle of sharpening of the drill and the presence of a safety cone. They are used for drilling shallow holes with further processing.
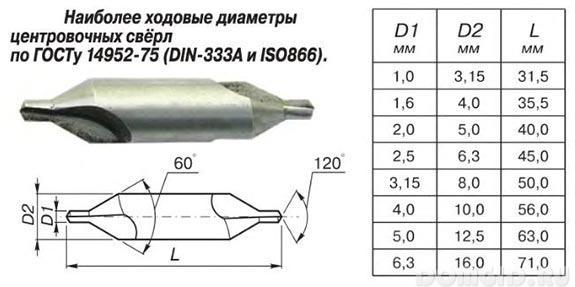
Single-sided drill Designed for drilling precise holes in metal. Often used in weapons manufacturing. The drill is hollow. The chips together with the coolant are discharged through the technological hole in the drill, which ensures high precision drilling. Used for drilling long and short holes. Provides low surface roughness. When working with this drill, a quick rotation of the tool and a slow rotation of the part in the opposite direction are recommended.

Conical drills designed for drilling in sheet metal up to 4 mm thick in various plastics, glass. Drills do not need preliminary alignment, have a smooth course of the cutting part.

Step Drills used for processing sheet metal, plastic, glass, marble. Possess the increased wear resistance of the cutting part, the increased term of operation. With their help, centering, drilling and deburring and burring are performed in one go.

Forstner Drill It is used for drilling holes in wood, plastic, drywall. As a result of using this tool, precise holes with the correct geometry and clean without scoring are obtained. These drills are equipped with four cutting surfaces: two main cutters and two undercutters. Ideal for drilling blind holes with a flat bottom.

Drills for drilling polyhedral holes used for drilling three-, four-, five- and hexagonal holes. The number of teeth in these drills is always one less than the number of faces of the hole.

Shank design
Shanks of drills also have differences, consider the design of shanks.
Straight shank used on all types of drills. In most cases, the diameter of the shank is equal to the diameter of the drill. It transmits a small torque due to possible slippage in the cartridge.
Tapered shank(Morse cone) is used in an industrial tool for fixing in machine chucks.
Triangular shank drills are easily clamped with a three-jaw chuck, eliminates the rotation of the drill in the chuck.
Square shank a drill with such a shank is inserted into the hole of the corresponding shape. Now practically not used due to poor fastening in a three-jaw cartridge.
Hex shank easily fixed in the chuck, eliminates slipping of the tool. Based on it, a special inch holder is developed for quick tool change. A disadvantage of the shank is a reduction in drilling accuracy when installing the tool in an inch holder, and not in the chuck.
Sds (Special direct system) shank developed by the company Bosch. This is a specially designed slot system for quick tool changes. Tool with shanksSDS are called Boers. The company has developed 5 varieties of shank:
- Sds shank with two grooves, fully compatible with SDS-plus .;
- SDS-plus the most common SDS type shank. It has four grooves, with which it is fixed in the cartridge. Shank diameter 10mm. It is used in all lightweight construction rock drills. The maximum drilling depth is up to 1m, diameter up to 26mm;
- Sds-top designed to solve the problems of failure of the drills of the SDS-plus system when drilling holes 16-26 mm. The shank is made with a diameter of 14 mm, which increases the reliability of the drill. To install the drill of the SDS-top system, you need to change the drill chuck.
- SDS-max Shank diameter 18mm. It is used in heavy punchers when drilling a hole with a diameter from 20 mm.
- Sds-quick Introduced in 2008. Instead of grooves in the shank, projections are used. It is applied to the Bosch Uneo puncher. Compatible with an inch holder.
Drill Materials
Drills are made solid or welded. For small diameters up to 8mm, drills are made whole. Drills of larger diameter are welded. The shank of the drill is made with carbon steel, and the cutting part with:
Carbon steel (U8, U9, U10, U12) for drilling wood, plastic, soft metals.
Low alloy steel (Х, В1, 9ХС, 9ХВГ) is used for the same materials, but has increased heat resistance (up to 250С) and the possibility of increasing the cutting speed.
High speed steel (HSS) are used for drilling steels in non-hardened version. Possess high wear resistance and heat resistance (up to 650C).
Carbide drills (T15K6, T5K10, VK3, VK8) drills with soldered carbide plates. They have great heat resistance (up to 950С) and wear resistance. Used for drilling concrete, stone, tile, non-ferrous metals, non-hardened steels.
Carbide drills(VK6, VK8, VK10M, VK15M, T5K12V) are made of steel with impurities of tungsten carbide, titanium and cobalt. It is used for drilling high-strength and hardened metals, non-ferrous metals, cast irons, stone, concrete. Drilling is carried out at low speeds.
Drill Covers
To improve the mechanical properties of the drills, they are coated with various materials that contribute to an increase in their strength and wear resistance.
As coatings or solders for the cutting part, use:
Black oxide film provides corrosion protection to the drill, increases the heat resistance of the drill.

Titanium nitride (TiN) golden or tan ceramic material. The coating is obtained by vacuum-plasma melting. Increases drill service life by 3-4 times. Drills with this coating cannot be sharpened.

Titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN) coating is violet-black, has heat resistance up to 950С and high hardness.

Titanium carbonitride (TiCN) coating is a bronze-violet color; the shade depends on the amount of carbon in the coating. One of the best coatings for cutting tools.
Borazon soldering on a tool based on boron carbide is inferior to diamond in hardness, and at the same time it has greater thermal stability than diamond. This allows you to increase the cutting speed and material processing.

Drills (drills) equipped with diamonddiamond-tipped drills are used for drilling tiles, glass, crystal, ceramic tiles, stone. When working with a diamond soldered drill, it should be remembered that there is increased heat generation in the cutting zone, which can lead to damage to the tool or workpiece. To remove heat, it is necessary to use coolant (cutting fluid). Diamond brazed drills are highly productive and require almost no sharpening.

Different materials different drills
This principle has become fundamental in the processing of materials. Consider where, what and how to use.
We work with metal
In most cases, screw drills are used to drill metal. They do an excellent job of this task. The drill is selected based on the metal in which the hole is to be drilled. It can be a drill with low alloy steel, and maybe with carbide material. For thin sheet blanks, you can use step drills.
We drill wood, plywood, chipboard and plastic
Drills for metal are also suitable for drilling holes in a tree. True, this does not guarantee the accuracy of the task. For accurate and high-quality processing of wooden surfaces, screw drills with a special centering tip and feather drills are used. Also for blind holes, the Forsner drill has been developed.
Drill concrete and brick
In the construction industry, so-called drills are used with SDS shank drills. Since concrete holds the compressive load well, concrete and brick drills work with shock-rotational movements, in this way painting the material and increasing the speed of work.
Other materials
Glass, tile, ceramic tile, crystal are fragile materials, drilling in them must be done only by the rotational movement of the tool. For drilling use augers with diamond brazing.

For drilling holes of large diameter, a ballerina uses a special drill for tile.

The industry also produces universal twist drills that can be used for various materials. Of course, no one will work professionally with them, but minor repairs in the apartment can be carried out.





