Search
Login
The root system of plants, how to correctly determine the size of the root system of the fruit tree, useful tips
A properly developing root system of a tree is the key to a successful passage of a plant through its entire life cycle. Since the normal development of the root is ensured by the quality of the soil, with the roots growing in its upper and lower layers, the care of plant roots in practice consists in the care of the soil, which is the environment in which the root system grows and develops. Knowing exactly how the underground part of each type of fruit tree is located in the soil is very important for the gardener - this information will allow for proper care of the plants, to observe the depth of the soil treatment, which would not lead to damage to the roots, especially the suction ones. Knowing the periphery of the near-stem circle, the gardener will be able to rationally apply fertilizers - they will immediately find themselves in the area of \u200b\u200bthe most active roots of the tree and also properly produce root watering.
Content
- The structure of the root system
- The size of the root system - what factors do they depend on
- Apple tree
- Pear root system - features video
- Which species of fruit trees should be preferred
- Root system of seedlings video
The structure of the root system
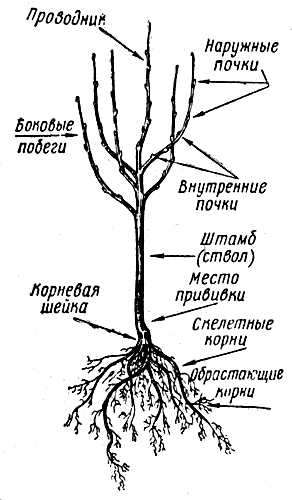
The root system of plants, in particular fruit trees, is their underground part, including the root neck, skeletal roots and fouling. The place of transition of the root into the stem is called the root neck, it has a transitional color, the color between the ground and underground parts of the plant changes smoothly. Only trees that have grown from seeds can have a real horse neck, plants propagated by cuttings or layering have a false root neck. When planting seedlings of fruit trees, it should be remembered that the root neck should be located above the surface of the soil.
The primary root and all branches extending from it take part in the formation of the skeletal structure of the root. The purpose of skeletal roots is to supply the tree with nutrients in the warm season and store nutrient reserves in the winter. Skeletal roots also serve to strengthen the plant in the soil. The growth they give is a natural way of plant propagation.
The root lobe of the tree is formed by their fouling roots, it represents the most active part of the system, serves to absorb and absorb moisture and nutrients from the soil and transfer them to skeletal roots.
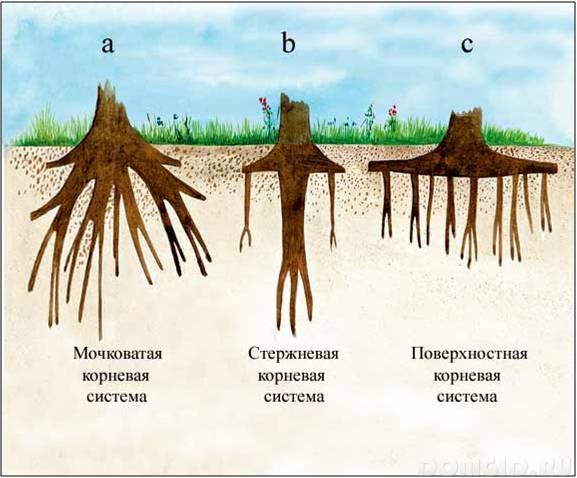
Types of root systems of trees for placement in the ground can be:
- vertical
- horizontal.
The size of the root system - what factors do they depend on
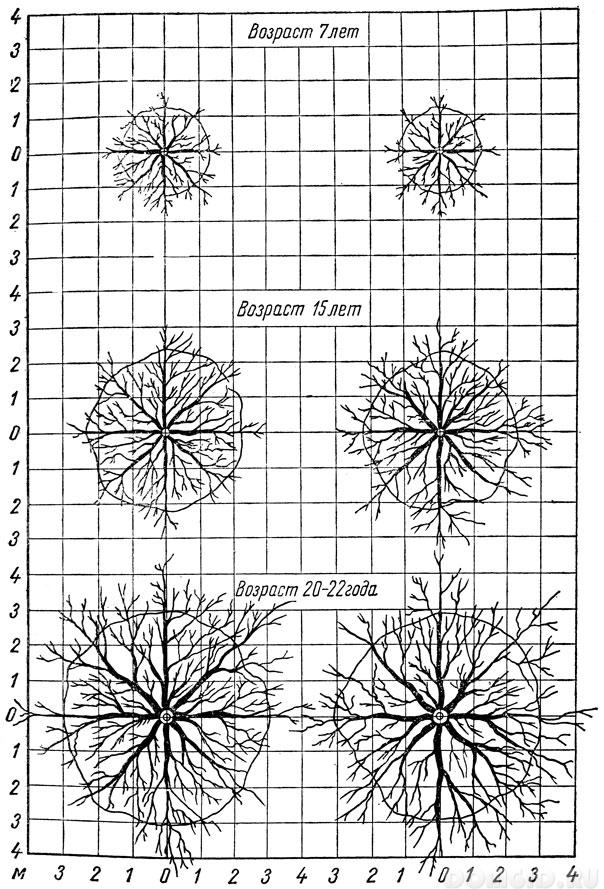
If the growth conditions are satisfactory, then the size of the root system of the tree can be quite large. In fruit trees, roots can penetrate 3-4 meters deep, they can branch 5-8 meters wide. But in most cases, the most active part of the root system is located at a shallow depth, on the order of 0.2-0.8 m.
It should be noted that the growth of the root system of fruit trees is a non-uniform phenomenon; during the year, two waves of enhanced growth can be observed: in autumn and spring. It is interesting that the ground part of the tree comes to life earlier in the spring, in the fall - first the growth of the shoots stops, then the leaves fall off, the growth of the roots continues for some period after the fall.
The rapidity of increasing the size of the underground part of the tree depends on the temperature of the soil, its saturation with moisture and air, nutrients. The soil temperature is considered optimal for growth from +7 C to +20 C, with a decrease in temperature below 0 or increase to +30 C, growth stops. The roots of shrubs and trees suffer from a strong drop in temperature to a greater extent than the crown. Therefore, in frosty winters should cover the basal area with peat, snow, spruce branches.
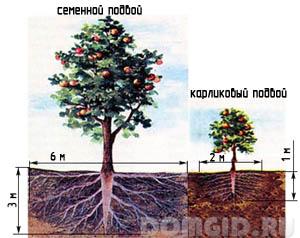
The level of oxygen saturation of the soil in many respects depends on the looseness of the soil, and excessive moisture, especially stagnant water, does not affect it in the best way. Inhibition of root growth contributes to the lack or excess of nitrogenous compounds in the soil. Potassium and phosphorus are useful for wood - they stimulate branching of roots, and calcium gives strength. The size of the root system of trees also depends on the type of stock. To contribute to an increase in the mass of roots below the arable horizon, it is possible by means of certain agricultural techniques, for example, planting plowing.
Typically, the depth of the root system of fruit trees is from 20 to 60 - 75 cm. As for the horizontal direction, they far exceed the crown projection on the ground. The Korean system of plums and cherries have a similar bedding pattern.
Apple tree
The root system of the apple tree is somewhat different, the bulk of the roots is at a depth of 50 to 60 cm, some groups of roots penetrate much deeper, up to 4 m. A more shallow occurrence of the root system is characteristic of the northern regions. For example, if the soil is moist and heavy, then the depth can be only 20-25 cm. But for the climatic zone of the North Caucasus, this figure will be about 7 m, if the radius of the crown of such an apple tree is equal to 1.5 m, then the lateral the roots can be spread out horizontally in a radius of about 3.5 m.
The depth of the shallow root mesh for such a tree will be in the range of 50-60 cm.
Pear root system - features

The pear tree has vertical and horizontal root systems, the roots of the first go to a considerable depth and have virtually no branches, the roots of the second, parallel to the surface of the soil, are very branched, but at the same time they have a compact arrangement and extend slightly beyond the crown projection. The horizons of the root system of pear trees are in deeper horizons than the roots of apple trees. That is why the pear is not inclined to give growth, this phenomenon is much more common in apple trees.
The greatest number of pear roots lies at a depth of 20 cm to 160 cm, and skeletal roots can grow to a depth of 5 m. For a pear with a round crown, the root system is usually wider and thicker than pyramidal trees. The activity of growth and placement of the root system in space is influenced by:
- rootstock,
- features of the grafted variety,
- environmental conditions
- tree age
- climatic conditions
- correct fit.

Of the features of the pear, it should also be remembered that when transplanting, it reacts very painfully to pruning roots. Sensitive to the state of the root system, the crown begins to fully develop only in the second year after the plant transplant, and then in the case of restoration of the root system. A tree with severely damaged fouling roots is almost doomed to death.
Which species of fruit trees should be preferred
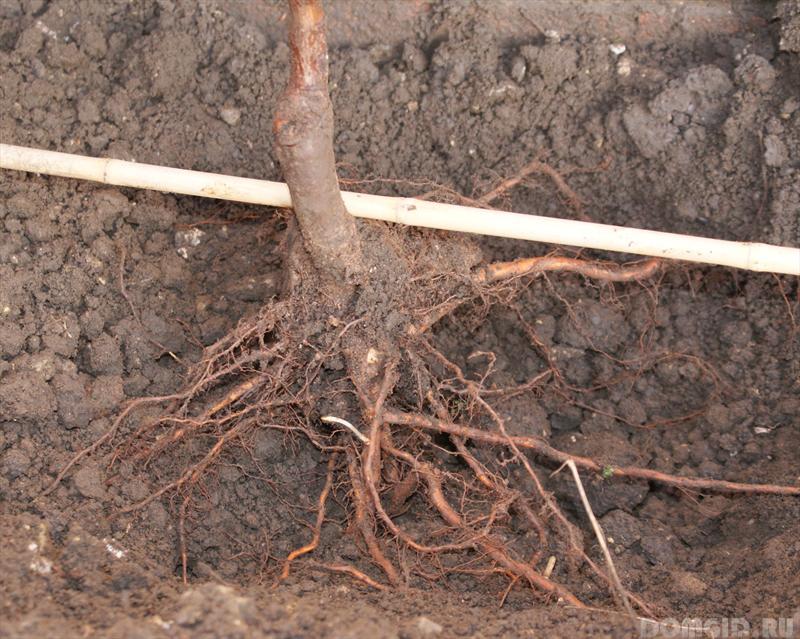

Numerous studies show that the size of the root system of fruit trees, starting from the second year and then about 1.5 - 2 times greater than the projection of the diameter of the crown. Moreover, such a proportion is observed in trees of different species growing in different climatic conditions. At the same time, with the shift of the horticulture zone to the south, a deeper occurrence of the underground part is observed. But with a high level of groundwater or the presence of dense pebble layers in the soil, trees in the southern regions can also have a surface arrangement of the root system.

When choosing a tree species, one should give preference to one that has a uniform root circumference, maximum deep and wide, allowing you to get the maximum amount of moisture and nutrients from the soil. A plant satisfying such requirements will be characterized by high frost resistance and resistance to drought. In addition, the lifespan of such plants will be longer, and their bearing will differ in regularity. Also, when planting a garden, one should take into account what root system will be in trees planted nearby - Darwin proved that there is intense competition between plants of the same species when grown together, but it is absent in plants of different species. Also, a more active distribution of roots will be observed in the direction of growth of a weaker neighboring tree.
Root system of seedlings

Since the development of the root system of a tree determines the duration of its life and the quality of fruiting, when buying seedlings, you should pay close attention to the roots. When buying a tree with an open root system, you need to make sure that it is sufficiently developed and dense. The tips of the roots should have a whitish hue - such plants have been dug recently and the growth of their roots continues.
Do not buy trees:
- with blackened and dried roots,
- with growths on the roots,
- with curved, deformed roots.
Caution should be given to trees with sluggish or dry foliage - perhaps the plants were kept untouched and their survival from this could significantly decrease.





